What is a disruptor?

What is a disruptor? You’ve probably heard the term used in business circles or in management training sessions. Perhaps you haven’t really thought too much about it or conversely, you may be longing to find out more about what a disrupter actually is. To understand what a disrupter is, we must first look at the idea of disruptive innovation.
According to The Economist, the idea of disruptive innovation is the most influential business idea of the 21st century. Coined in 1995 by American academic and business consultant Clayton M Christensen, the idea of disruptive innovation has been applied to a diverse set of industries both in modern society and historically.
To be a disrupter is to create a product, service, or way of doing things which displaces the existing market leaders and eventually replaces them at the helm of the sector. Disruptors are generally entrepreneurs, outsiders, and idealists rather than industry insiders or market specialists. Disruptors are often linked to the fast-moving technology industry but can be found in almost any area of business.
How does a disruptor succeed?
You’d be forgiven for thinking that a disruptive idea takes the existing market by storm almost instantly, making dramatic changes overnight. In reality, the opposite is true. Disruptive technology is successful over a significant period of time. First, the disruptor must gain a foothold in the market from where to progress. The new product or service is initially realised and released into the low end of the market.
Once the disrupter has a foothold with the least profitable section of the market, they seek to penetrate the medium and higher quality portion to increase profit margins. Eventually, the disrupter will challenge the most profitable part of the sector by offering a new alternative to the established market favourite. The existing market leader is then driven out of the market as the demand for their product/service disappears.
As you can see, disruptive innovation does not refer to one product or service but to the evolution of a disrupter within a market arena over a period of time.
Digital disruption
An excellent example of successful disruptive innovation is in the way music is now consumed. For the majority of the 20th century, music was bought from record stores in the form of vinyl, cassette tapes, and CDs. In the 1990s, as the internet became more popular, file-sharing technology emerged which gave internet users free access to their favourite music.
Initially, low-end disruption of the way music was consumed existed alongside the traditional methods of music purchase and consumption. Over time, illegal file-sharing became better regulated and was replaced by online retailers such as iTunes, Spotify, and Amazon who revolutionised the way music is consumed. Legal music downloads and online streaming now accounts for over half the revenue made by the music industry.
Music consumption is also the perfect way to illustrate the transitional nature of disruptive innovation. In the music industry, we have actually come full circle with sales of vinyl records at their highest since before they were replaced by the cassette, CD, and eventually the download. This highlights the unpredictability of consumer trends and how human factors play the most important part in every area of business.
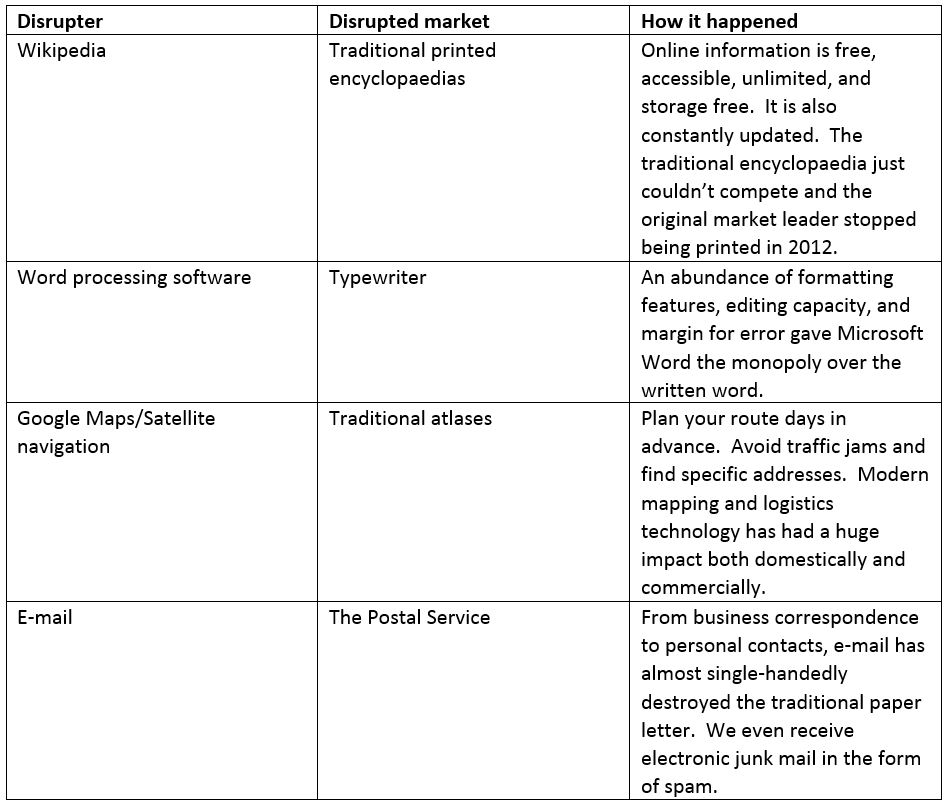
Some examples of successful disruptors
From IT, social media and the digital world to manufacturing, medicine, and transport, a disrupter can find success in any market. Here are some excellent examples of successful disrupters and the markets they disrupted.
The future of disruption
Disruptive innovation is here to stay. As modern technology advances at a staggering rate, the opportunities for disruptive innovation continue to increase. 3D printing is already having a massive impact on the traditional manufacturing industry while the cryptocurrency revolution is well underway through the increased use of PayPal, Bitcoin, and Contactless payments.
From our current perspective, space travel is perhaps the final frontier of disruptive innovation. And it’s already happening, as private enterprises backed by wealthy and visionary disruptors compete against world government agencies for the galactic marketplace. Whether it’s Elon Musk’s trips to Mars or Richard Branson’s asteroid mining is yet to be seen.



